3D printing process explained – in simplified terms
What is 3D printing?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a digital model. From the design and specifications from a digital model, raw materials such as plastic are ‘printed’ on a separate device, usually layer by layer. This build-up by layers process of manufacturing is different from traditional forms of manufacturing where objects are usually made from a mould. This eliminates the expensive tooling, fixtures and assembly usually required in traditional manufacturing. In addition, it also reduces the waste of raw materials from traditional moulds, where only a fraction of the material from a mould is used.
While there are many types of 3D printing and different software used, the process can essentially be boiled down into the following.
Design
Firstly, an object’s model must be uploaded on a Computer Aided Design (CAD) software or even drawn from scratch. The software stores all the specifications of the model and can assist in spotting errors that may interfere with the printing. The design is then stored as a computer file. This process is extremely beneficial for prototyping products because changes can be made immediately to the object and there is no waste from mass producing experimental products.
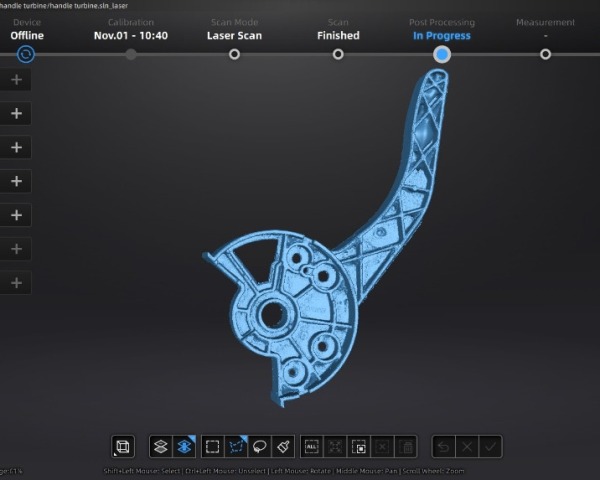
Scan
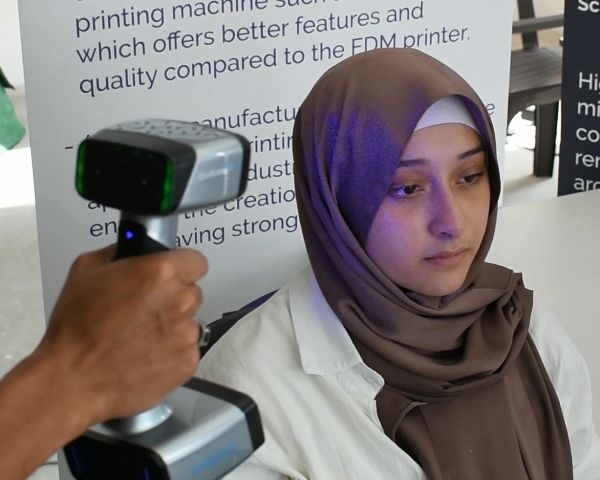
Besides the creation of model objects, it is also possible to scan existing objects onto the CAD software. This process is known as 3D reverse engineering, where a perfect reconstruction of the original design can be done. Once scanned, it is possible to replicate the object as it is or even to make changes to it via the software.

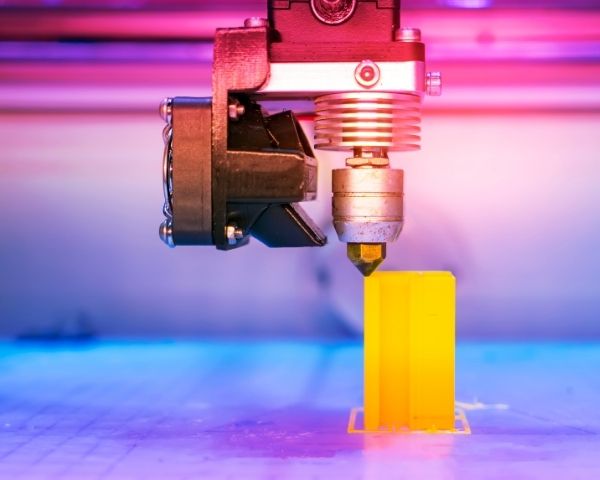
Once the computer design is finalized, the file is then sent to the 3D printer where it will read the instructions and specifications of the object and begin printing. Typically, 3D printers build objects by depositing layers of material onto a surface. The 3D printer will build the bottom layer first, after which it will build the next highest layer. There are different materials used to build objects, although thermoplastic is the most common material used for this process. One of the more commonly used form of 3D printing is called fused filament fabrication, or fused deposition modeling (FDM). Here, thermoplastic filament is fed from a large spool through a moving, heated printer extruder head and is deposited on the object layer by layer. Once printed, the object is finalized via using solvents to eliminate any imperfections or even removing any supports if they were used.

While this is a simplification of the processes involved in 3D printing, it describes what is essentially a revolution in traditional manufacturing, where possibilities are not limited by cost or complexity.

Gaia Pebbles is your go-to for all things 3D printing – be it designing, reverse engineering and printing. We customise for various end-consumer and business needs. Contact us for more information today!


